MACROECONOMIC OVERVIEW
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
TOPICS
- Growth is most broadly measured by Gross Domestic Product – the rate of change of growth determines expansions or recessions.
- Inflation is the rate of change of the defined basket of goods, or services.
- Labor Market activity is measured by unemployment rate, labor force participation rate, or quit rate.
- Fiscal & Monetary Policy are ways for government organizations to directly or indirectly stimulate economic activity.
- Legal and Regulatory Framework.
REAL AND FINANCIAL ECONOMY
Real Economy:
The real economy focuses on the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It deals with tangible products and activities that satisfy human needs and desires.
Financial Economy:
The financial economy deals with the exchange of financial assets and instruments, including stocks, bonds, loans, and derivatives.
REAL ECONOMY – WHAT PEOPLE DO
Real economy refers to the current and future activities of individuals and firms
Buying houses and cars or producing houses and cars
Participating in the labor market as an employer or employee
Business operations of public and private firms which result in revenues and expenses
Spending and saving by firms and households
Innovation, Expectations, Sentiment
FINANCIAL ECONOMY – WHAT PEOPLE OWN
Financial Economy refers to the assets and liabilities of firms and individuals
Houses, Office buildings, and Art are real assets
Common Stock in a firm or a Mortgage-backed Security are financial assets
Interest Rates, Discount Rates, and Expected Value of Future Cash Flows
HOW WE INTERPRET THIS INFORMATION TO MAKE INVESTMENT DECISIONS
We are constantly observing signals in the real economy and comparing that information to the price signals in financial markets.
By synthesizing these data points, we make asset allocation and security selection decisions to build diversified portfolios depending on each client’s specific needs and circumstances.
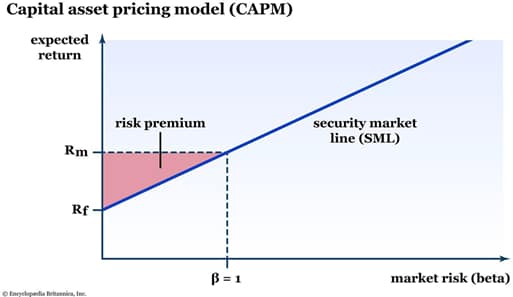
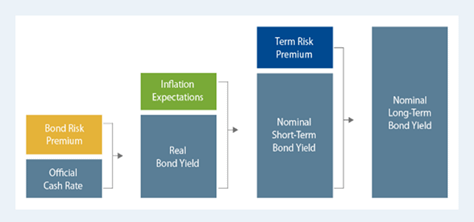
COMPONENTS OF BOND RETURNS
Interest rate components: Term Premium, Inflation Premium and Risk Premium
COMMON STOCK RETURN VALUATION
Equity Valuation: The current share price generally incorporates all expected future cash flows though market prices tend to oscillate around fair value.